A Product is More Than its First Life
- its Circular Potential Shows the Possibilities Beyond.
A product’s circular potential is defined by the number of alternative disposal options that can be identified for its materials.
It serves as consumer information – highlighting the added sustainable value that extends beyond first use.
Types of disposal alternatives - exploring circular possibilities.
Reuse
Everyday ways to pass things on – by trading, selling, or sharing them.
Refurbish & Resell
Professional secondhand loops powered by take-back offers from brands and retailers.
Hacks
Creative repurposing of products or individual parts for new uses.
Remanufacturing
Integrating used parts into new products as part of a planned circular design by the original manufacturer.
Upcycling
Individual DIY projects – creatively repurposing the materials within.
Mass Upcycling
Systematic reuse of materials at scale – based on collective design and practical demand.
Urban Mining Structures
Connecting local material needs with recovered resources – preparing reclaimed resources for new use.
The more disposal alternatives a product offers, the greater its circular potential.
It highlights what lies beyond the obvious - encouraging choices that support circular use.
Visibility Matters
- what Remains Unseen, Remains Unused.
Helping consumers embrace a more sustainable lifestyle.
Products often hold valuable materials for reuse – yet much of this potential is lost due to lack of visibility.

we
develop
reveal
enhance
circular potential
We translate circular choices into clear, actionable options – matched to each product and made for real-life decisions.
Making circular potential visible - how we do it.
Using our mapping logic, we match each registered product to reuse options that fit its profile – determined by the type and amount of material it contains.
After-use possibilities are clearly displayed, tailored to each product, and instantly available through our web app – ready to put into action.
Real potential, instead of abstract theory.
When circular potential becomes visible, it empowers mindful consumption and fuels local circular economies — in ways that are practical, understandable, and effective.
From concept to creation:
A disposal alternative found via the web app is put into action – and a discarded sofa cover transforms into a stylish waist bag.
Boosting Circular Potential
- by Combining Systemic Drivers and Product-Specific Insights.
1. Product Characteristics
The design of a household product primarily determines how many follow-up product ideas can be derived from it – especially through modularity and the ability to disassemble it into individual components.
The more modular a product is, and the more easily it can be broken down into large material parts using standard household tools, the better its chances for reuse.
Other relevant factors include:
- The number of different material types
- The dimensions of extractable materials
- The overall quality of the materials
Circular potential is initially measured by the number of possible disposal alternatives - but its realization depends on people’s skills and the local context.
2. Individual Skills
We provide the inspiration for follow-up product ideas – but can users actually bring them to life?
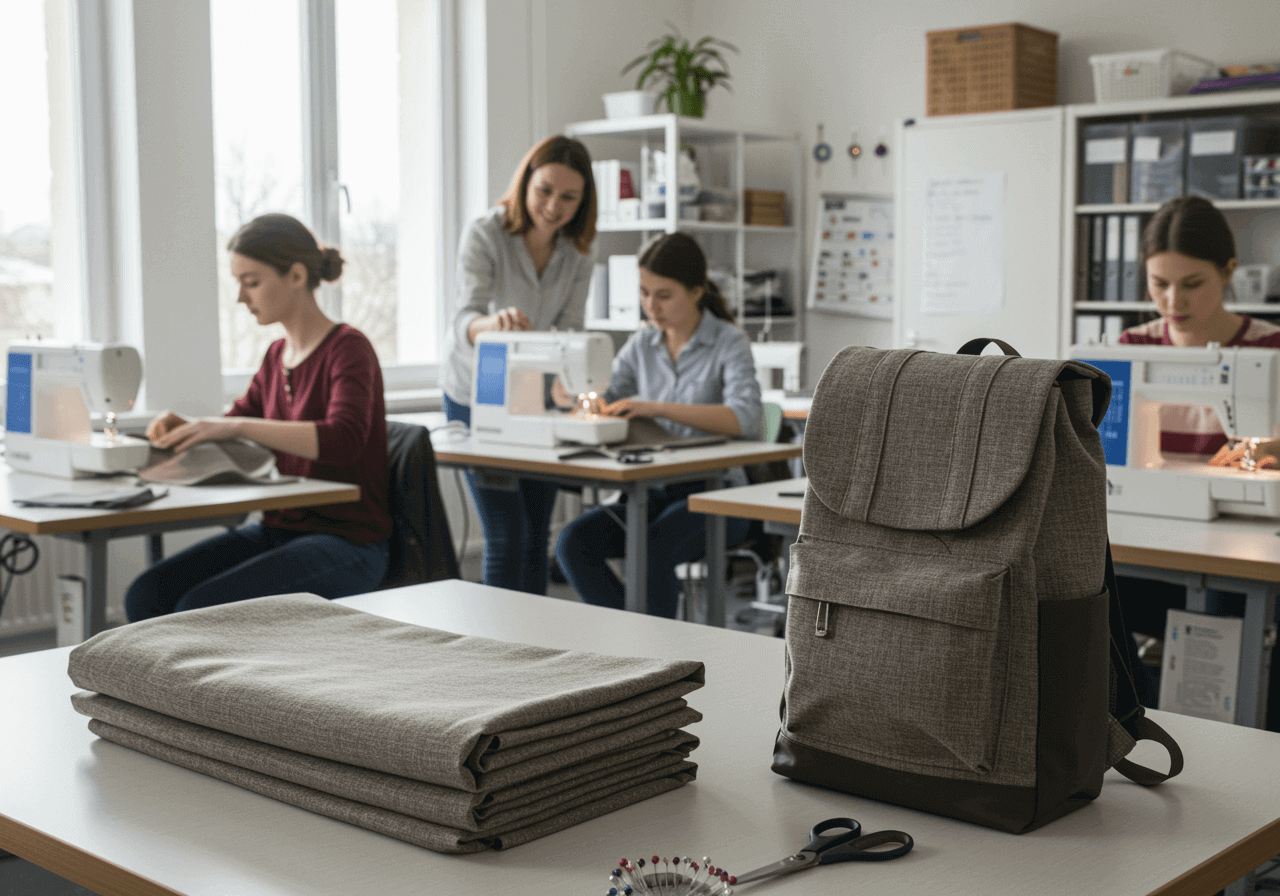

Not everyone has the craftsmanship, tools, or space needed for every step of the process.
That’s why a supportive network is essential:
People who share their knowledge, lend a hand, or take on the implementation themselves.
This way, materials stay in the loop – even when individual skills fall short.
3. Regional Opportunities
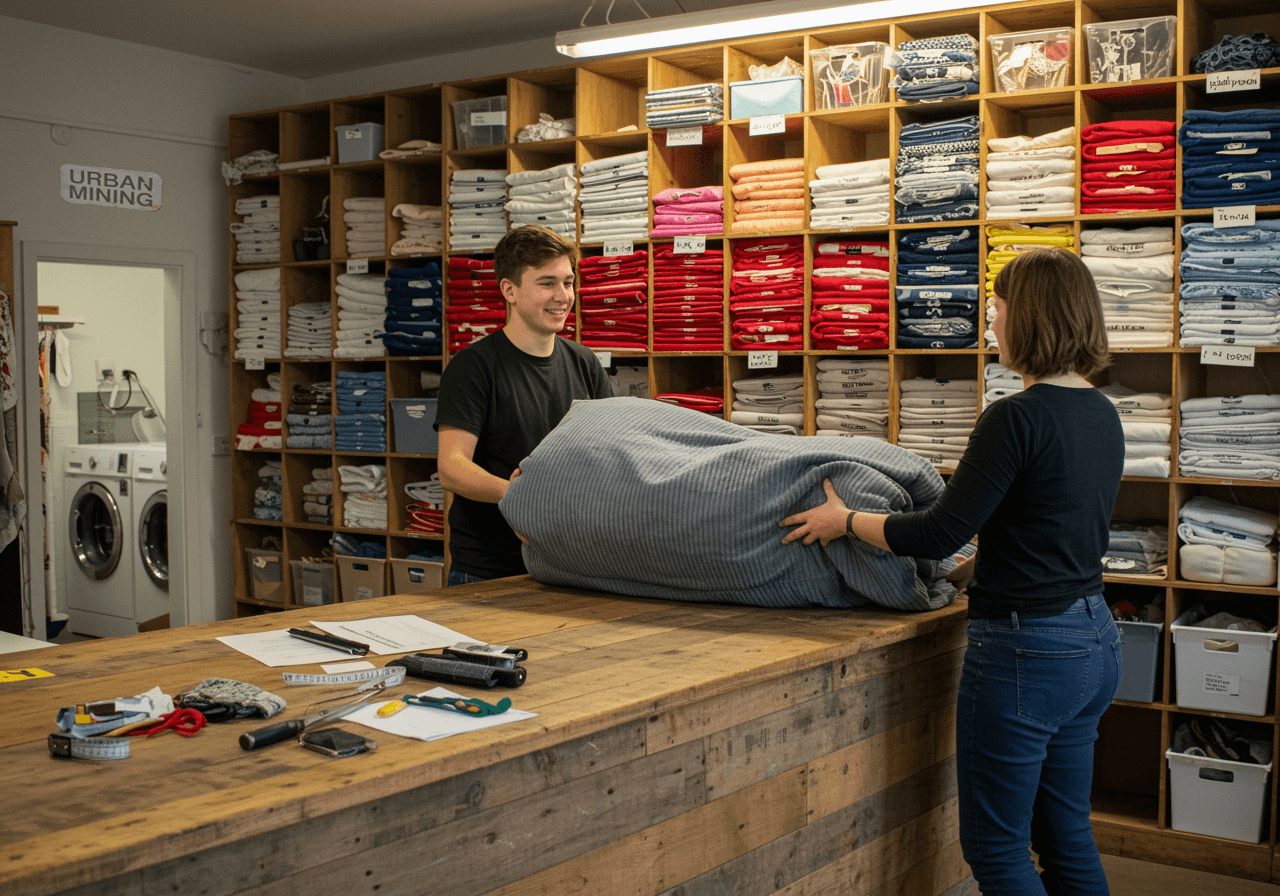

The better the regional setup, the greater the impact of circular potential.
Urban mining structures create spaces for material drop-off, disassembly, and redistribution.
Municipal involvement, hubs and local partnerships unlock hands-on access to tools, skills, and spaces – turning potential into practice.
Circularity Takes a Collective Effort
- it Doesn’t All Have to be Done at Home.
Circular potential is more than product-based inspiration for reuse.
It aims to inform consumers by evaluating both product features and, in the long term, also the local infrastructure needed to keep materials in circulation.
The goal is to make material reuse a shared, local experience — as part of a circular everyday culture.
A core element of mass upcycling.
Three Steps Toward an Active Circular Economy
What options are generally available for keeping materials in the loop after product use?
Summed up, what disposal alternatives are currently available – matched to the product and ready for local fabrication?
Local infrastructure and suitable product characteristics make it easier to reuse valuable materials – and significantly increase the potential for individual realization.